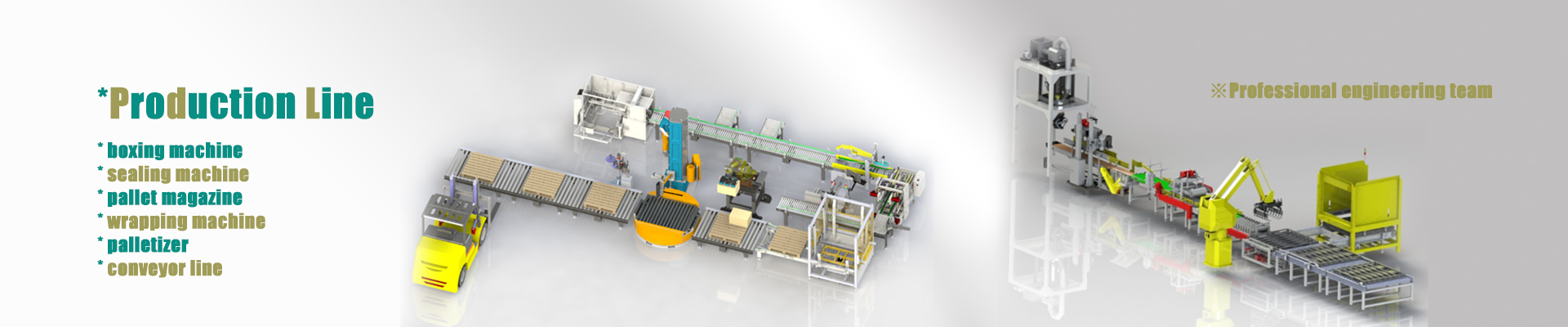
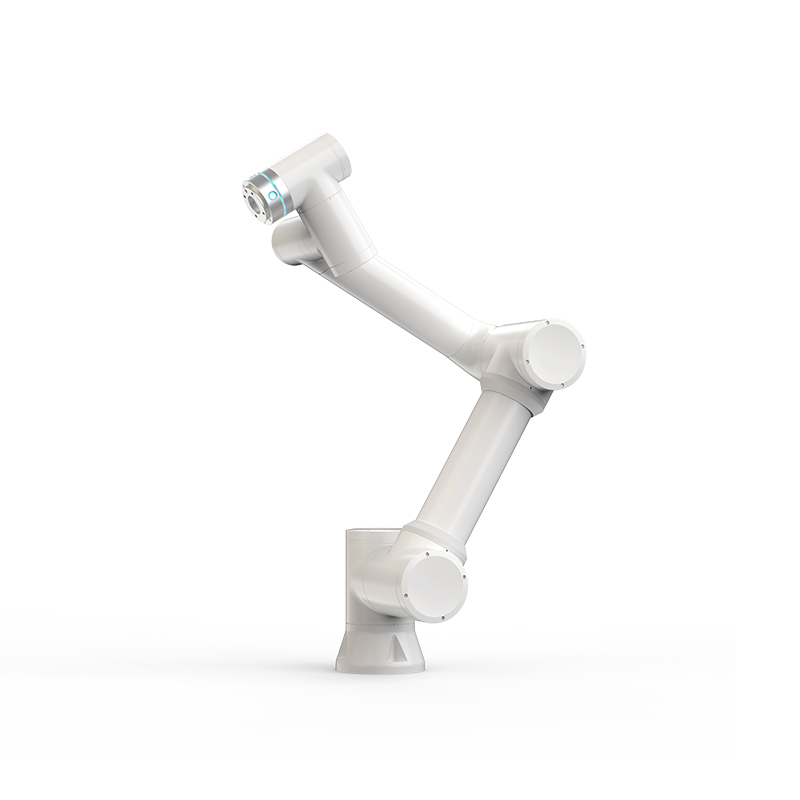
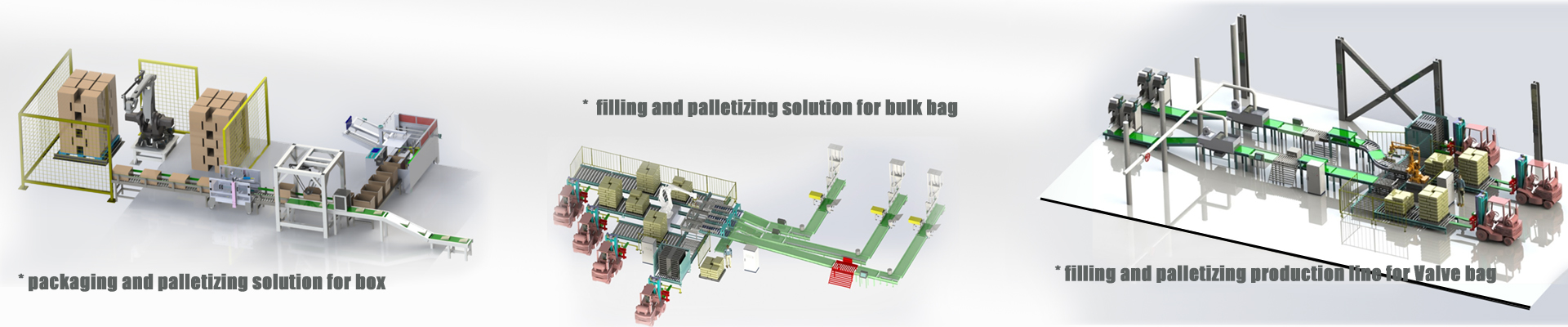
Structural design of integrated collaborative palletizing robot
Integrated system architecture: This robot integrates core components such as mechanical structure, power system, control system and sensor. This compact design not only reduces complex external wiring and connection, avoids failures caused by aging and loosening of lines, but also greatly improves the stability and reliability of the equipment. The entire robot has a simple structure, which can effectively resist the interference of adverse factors such as dust and moisture in complex industrial environments, ensuring long-term stable operation.
Arm structure: The arm is the main part of the robot arm, generally made of high-strength aluminum alloy or carbon fiber and other materials. These materials are light in weight and high in strength. While reducing the weight of the robot arm, they can withstand the weight of the goods and the inertia force during handling. The shape design of the arm has been optimized, and some adopt a hollow structure, which not only reduces weight without affecting strength, but also provides wiring space for internal cables and air pipes, avoiding interference and damage risks caused by external wiring.
Stable base: It is generally welded with heavy cast iron or thickened steel plates. The bottom is usually designed with anchor bolt holes to firmly fix the robot to the ground to prevent movement due to vibration or unbalanced load during stacking. The base may also integrate some components of the power system and control system, such as power modules, drivers, etc. Through reasonable layout and heat dissipation design, these key components can be ensured to work in a stable environment.
Motor and driver: Each joint is driven by an independent motor. The motor type is selected according to the load and motion requirements. The most common ones are servo motors. The servo motor has high-precision position control, speed control and torque control capabilities, which can meet the strict requirements of the stacking robot for motion accuracy. The driver matches the motor, receives the instructions of the control system, accurately controls the operating parameters of the motor, and realizes the precise movement of the robot arm.