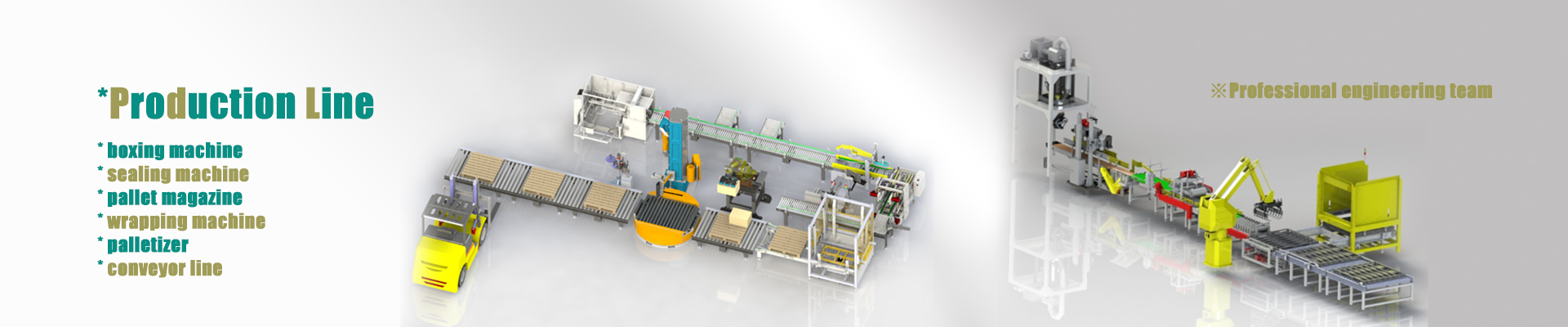
Working principle of paste filling machine
Metering principle:
Piston metering: This method realizes quantitative filling of paste by reciprocating motion of piston in cylinder. When piston moves upward, paste enters the space below piston under pressure; when piston moves downward, paste is squeezed out through filling head into container. The stroke of piston determines the filling volume, and high-precision metering can be achieved by precisely controlling the stroke length of piston. For example, in the filling of pharmaceutical paste, the filling error can be controlled within a very small range each time to ensure the accuracy of drug dosage.
Screw metering: Screw metering uses the rotation of screw to push paste from storage container to filling head. The pitch and speed of screw are key factors affecting metering accuracy. When the screw rotates at a certain speed, the paste moves forward evenly along the axial direction of screw under the action of screw, and the filling volume is determined according to the set number of screw rotations or time. This method is suitable for pastes with good fluidity and relatively low viscosity, such as some cosmetic emulsions.
Peristaltic pump metering: Peristaltic pump metering is a good choice for pastes containing granular components or sensitive to shear force. The peristaltic pump squeezes the elastic hose through the roller to make the paste flow forward in the hose. Its metering accuracy depends on factors such as the pump speed and the inner diameter of the hose. By accurately controlling the speed of the peristaltic pump, more accurate filling volume control can be achieved.
Filling process: First, the packaging container is accurately positioned under the filling head through the conveying system. Then, according to the selected metering method, a certain amount of paste is transported from the storage tank to the filling head through the pipeline. The design of the filling head is optimized according to the shape of the container and the characteristics of the paste to ensure that the paste can flow into the container smoothly and avoid splashing or bubbles. After the filling is completed, the filling head will stop the outflow of the paste in time to prevent dripping.