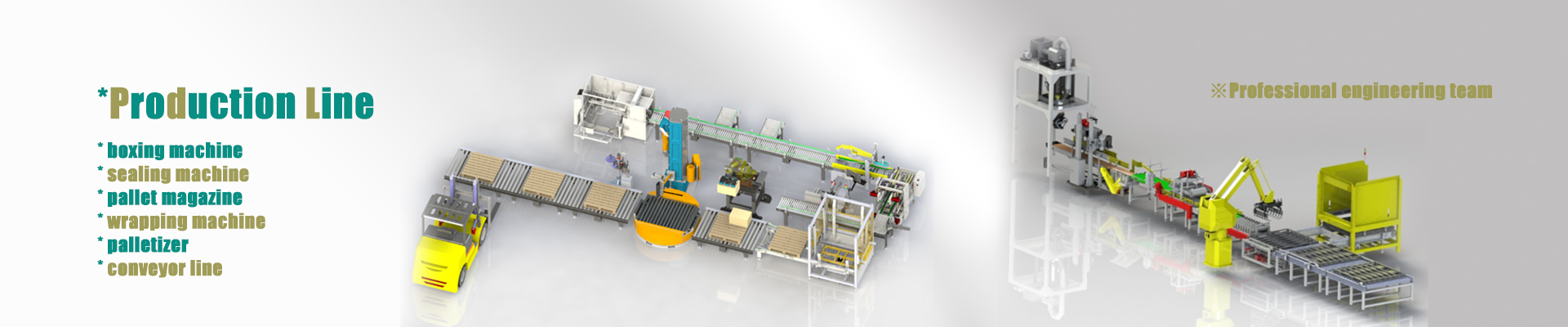
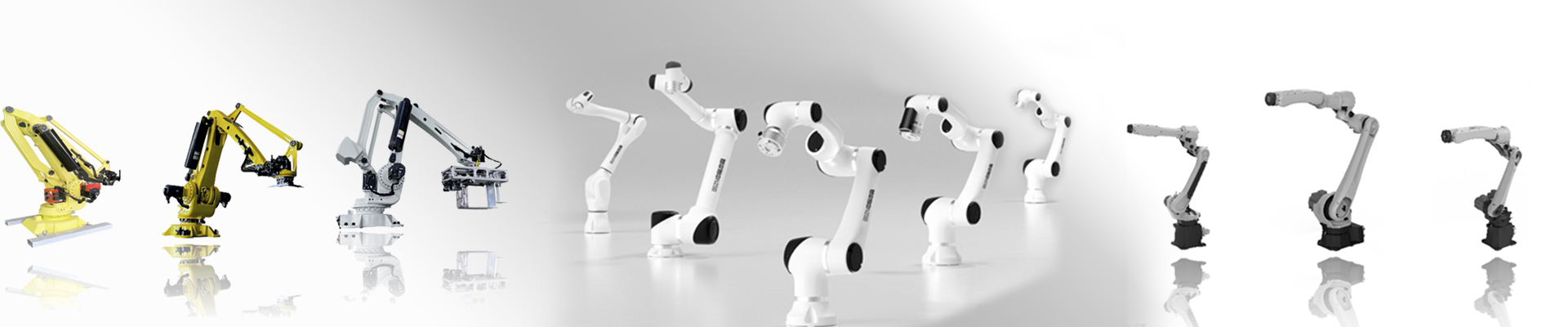
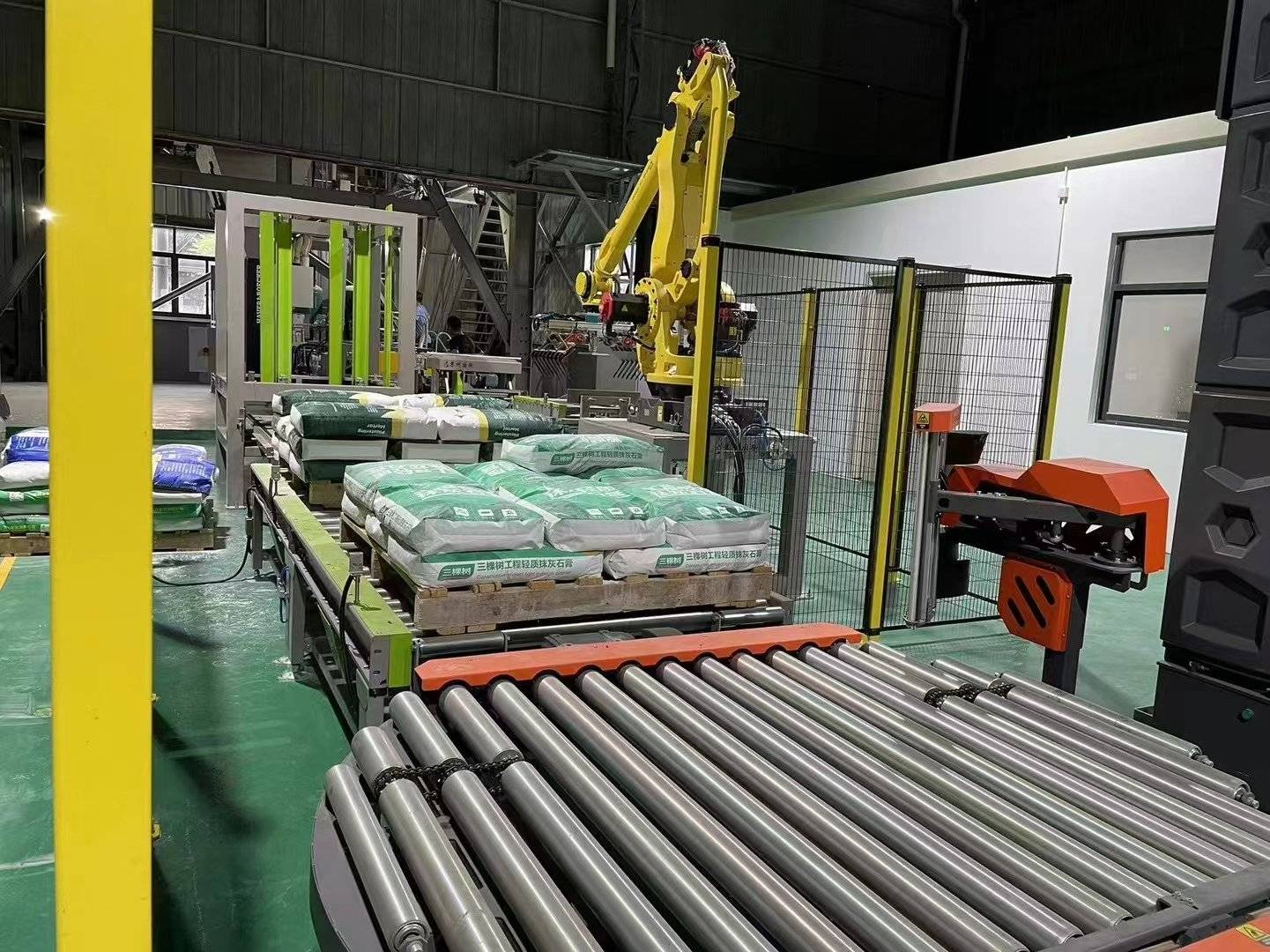
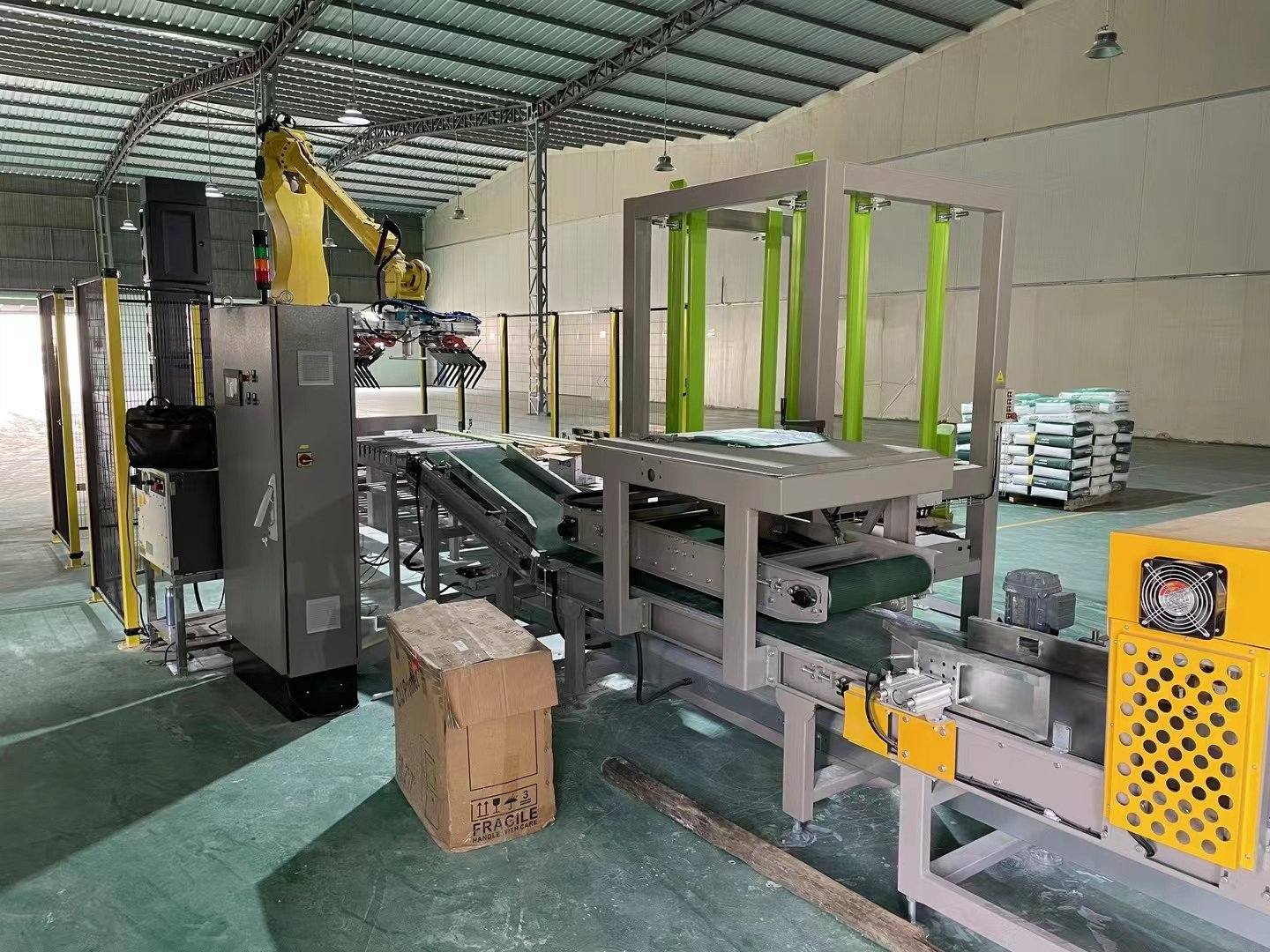
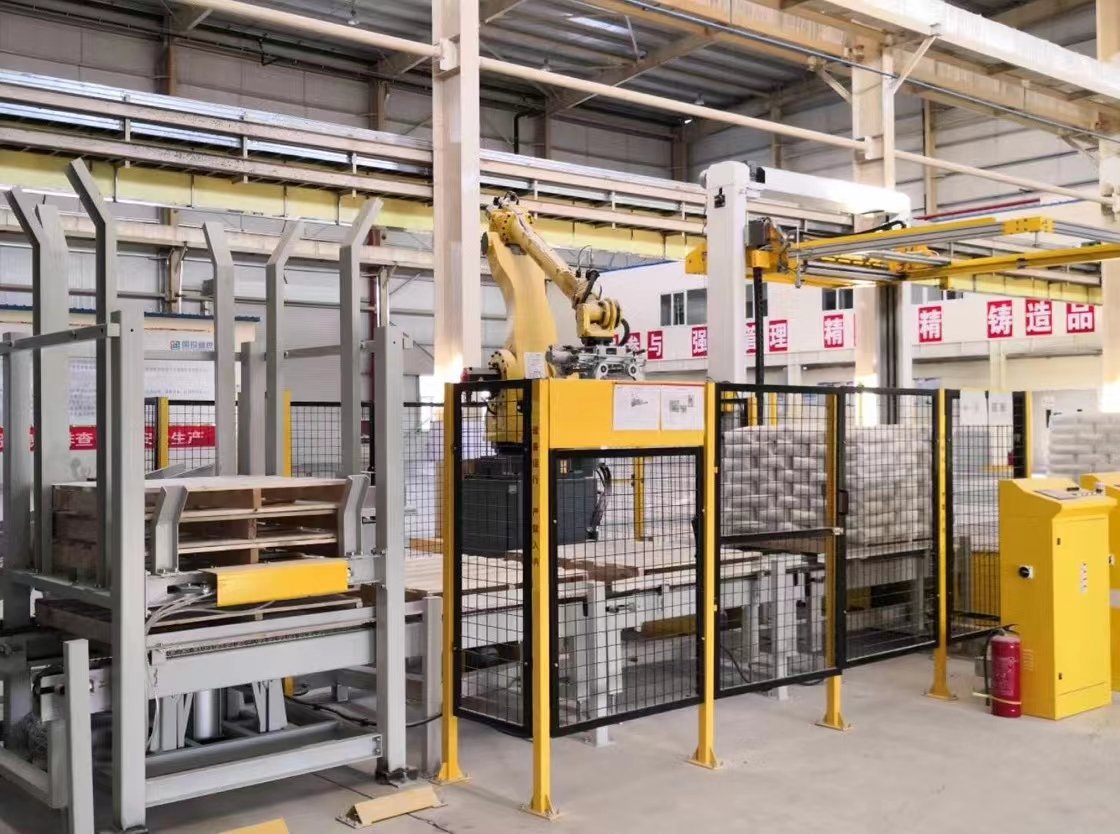
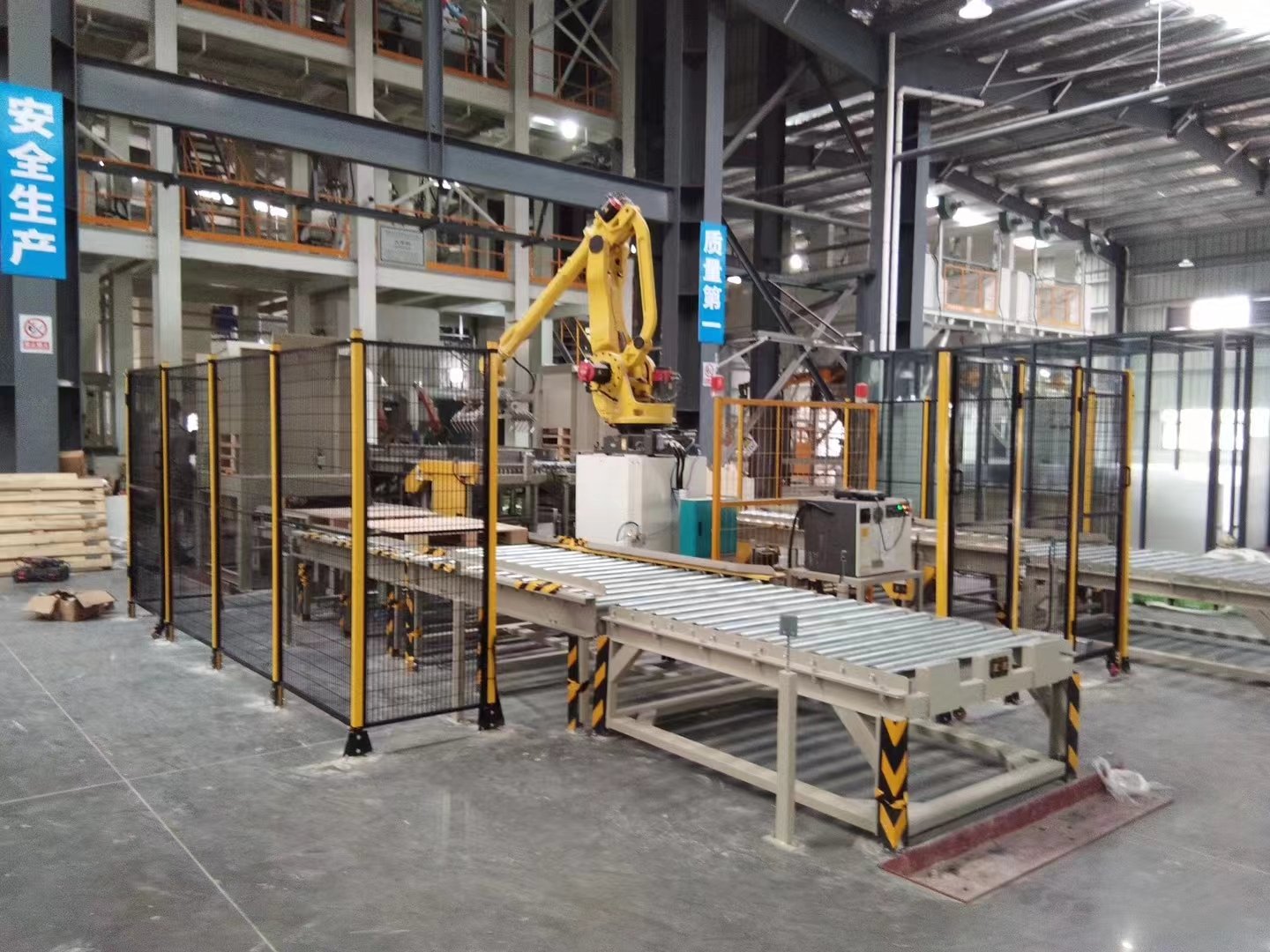
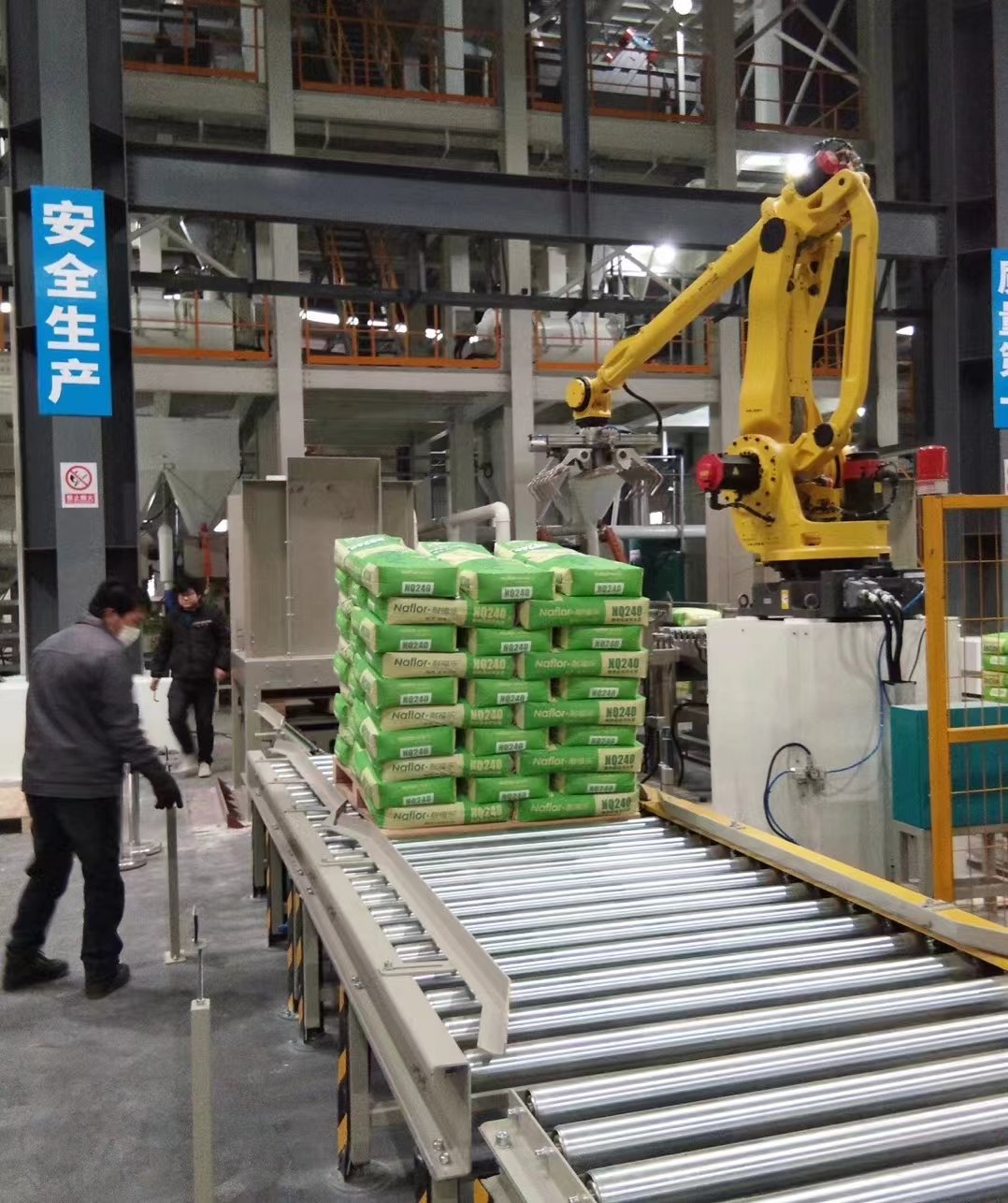
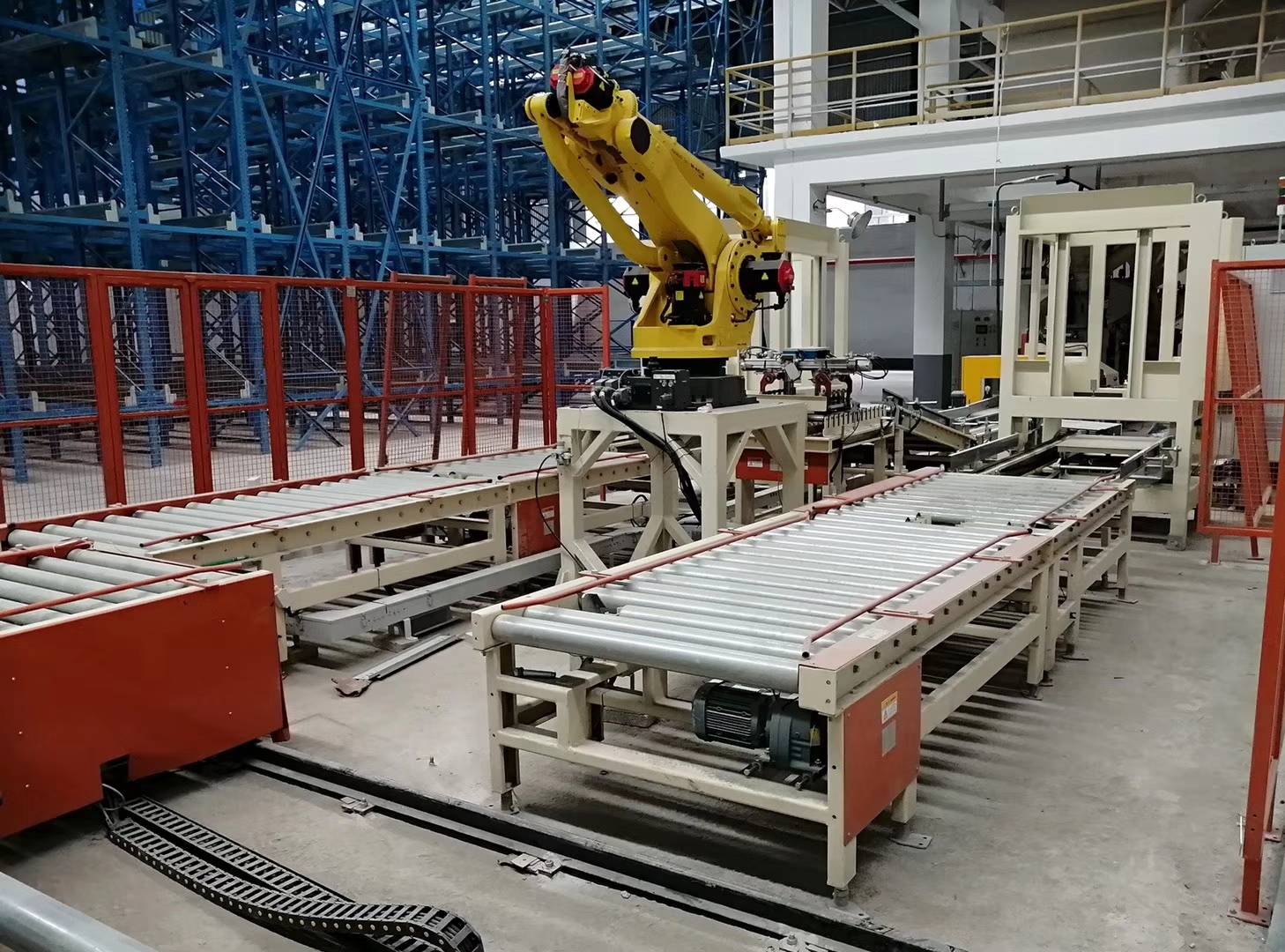
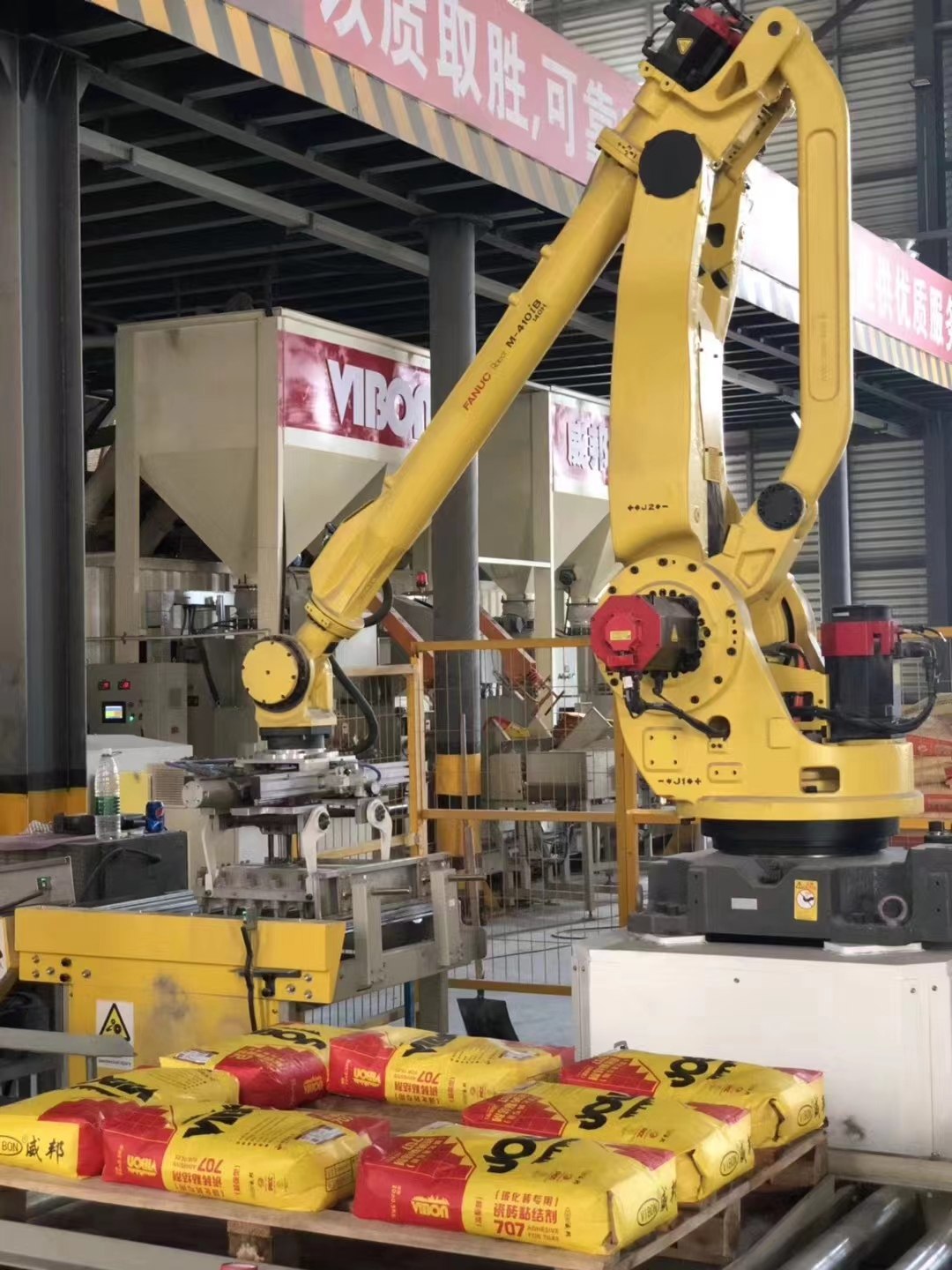
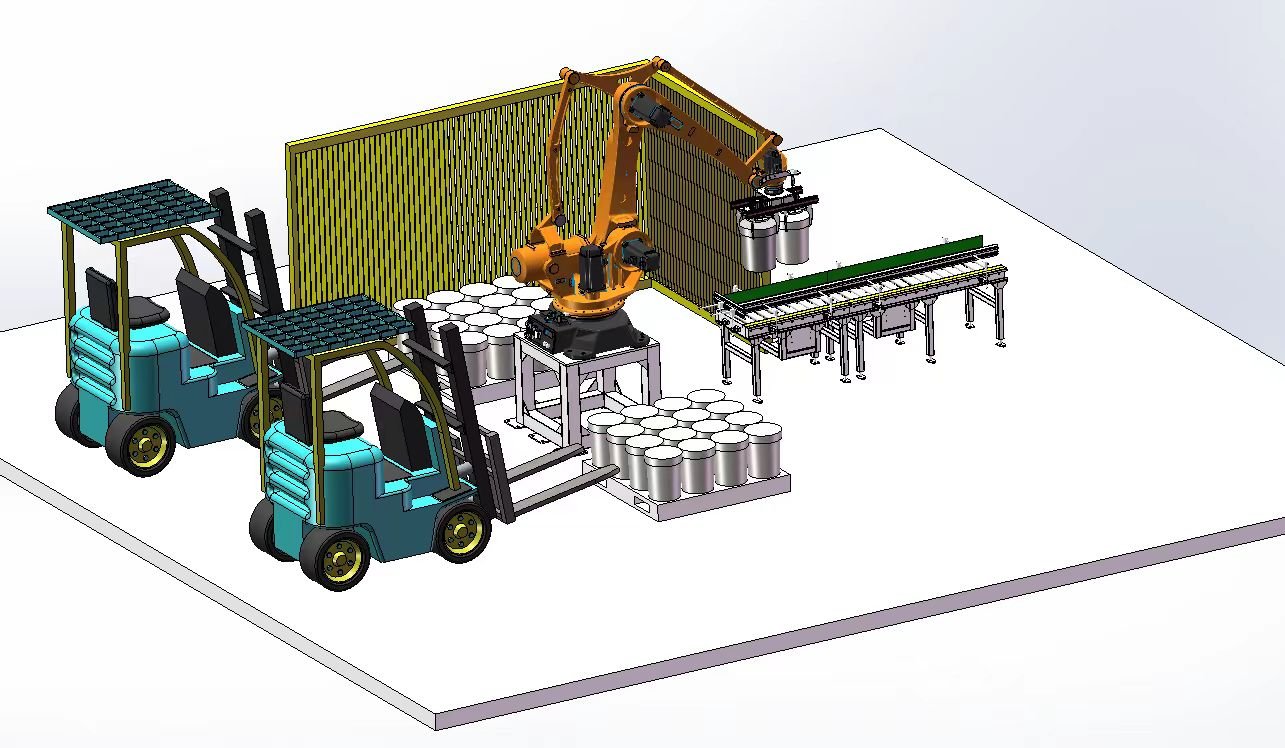
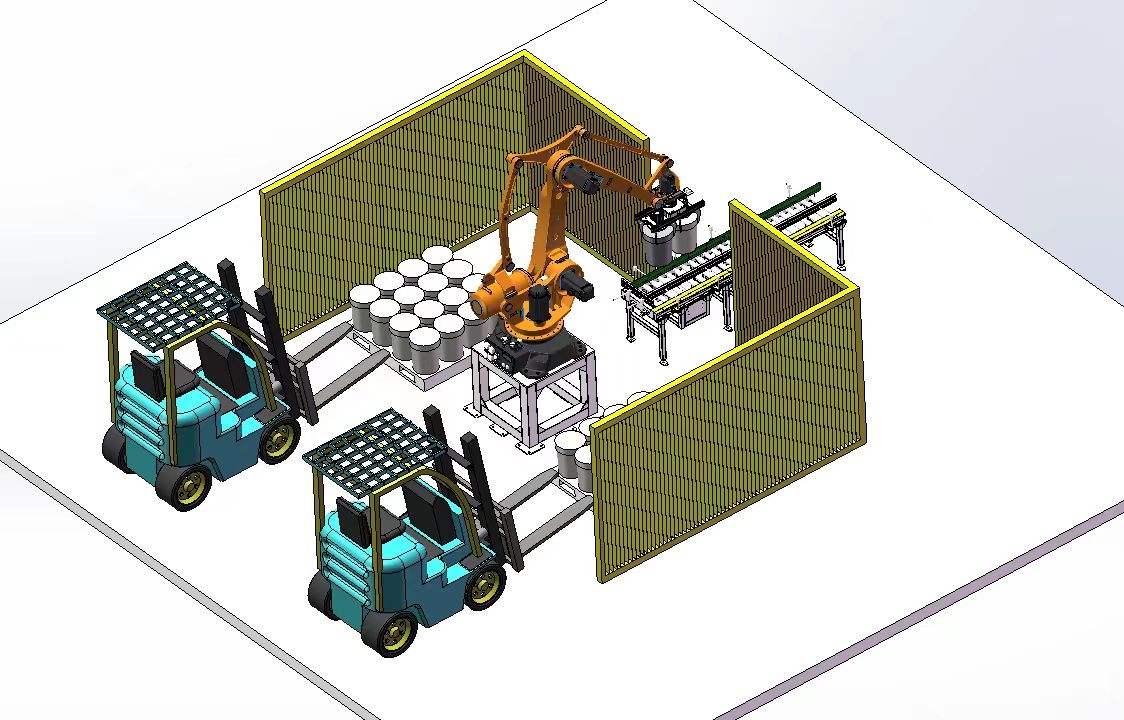
Automatic joint palletizer
The multi-jointed machine is similar to a human arm and is characterized by its ability to move flexibly like a human hand. For example, when encountering an obstacle, the multi-joint robot can bypass the obstacle to reach the target, which is difficult for the general polar or cylindrical coordinate type industrial robot. If some special movements (crank motion) are required to be completed, the multi-joint robot is also easier to complete. A multi-jointed robot can also move from one point to another in as little time as a human hand. If a multi-jointed robot is equipped with tactile and force sensors in its hands and wrists, it can do more and more complex work.
When a joint in the arm of a multi-joint robot rotates at an Angle, the other joints and their connecting rods will produce a movement in space. Accordingly, the claw reaches a new position, and the direction (attitude) of the position is also changed. Therefore, the general multi-joint robot needs to be controlled by computer. The robot has Angle detectors on each joint. Given the rotation Angle of each joint, the problem of obtaining the spatial position and attitude of the hand claw is called the analysis problem of motion control. On the contrary, given the position and attitude of the hand claw, the problem of how much Angle each joint connecting rod should rotate is called the synthesis problem of motion. The key to these problems is how to use the computer to carry out the above transformation and calculation.